29 814 47129 29 814 4712º 0 0î km ů 2 1748 2 174ỹ 0 02 km s the moon which has a mass of 7 347x1022 kg has the following radius and velocity vectors relative to the center of the earth.
Velocity of geostationary satellite with respect to earth is.
The gravitational force between the satellite and the.
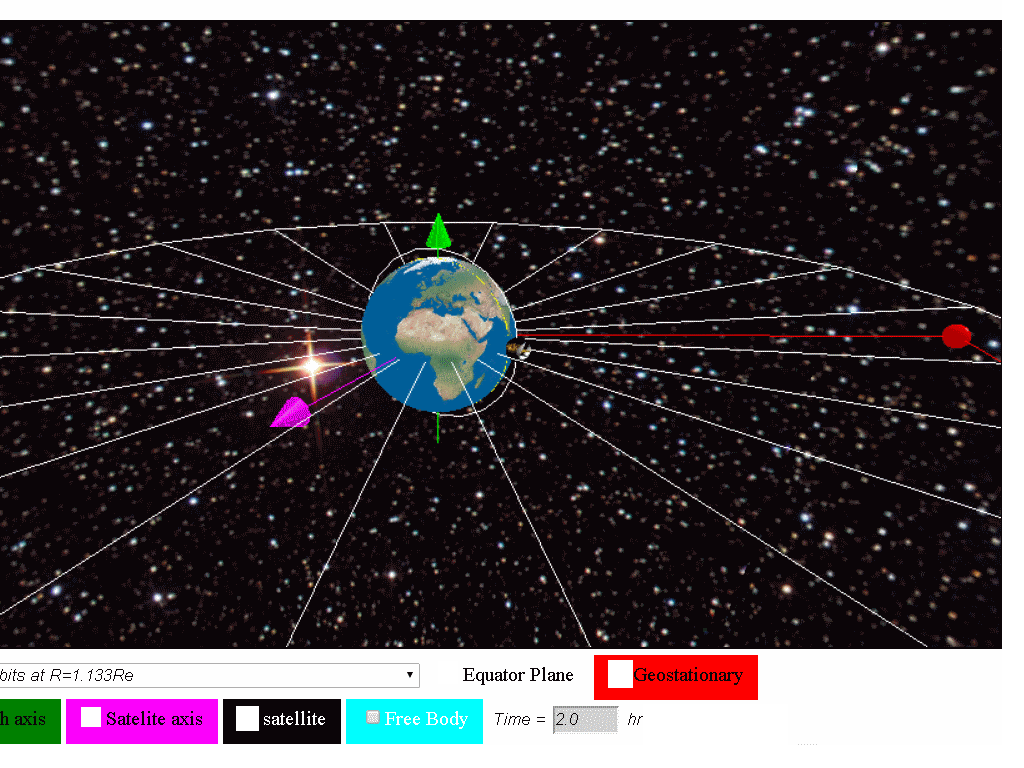
Those with inclination 0 form a diagonal belt across the image.
Since angular velocity of satellite about earth is same as angular speed of earth about its own.
To be geostationary a satellite needs to revolute at the velocity of about 11060 km h or 3075 m s.
ř 363 625 0.
The geostationary orbit is a circular orbit directly above the earth s equator.
R orbital radius earth s equatorial radius height of the satellite above the earth surface r 6 378 km 35 780 km r 42 158 km r 4 2158 x 107 m speed of the satellite is 3 0754 x 103 m s.
Circular orbit above the earth s equator and following the direction of the earth s rotation two geostationary satellites in the same orbit a 5 6 view of a part of the geostationary belt showing several geostationary satellites.
A satellite in this orbit is known as a geostationary satellite and has an orbital period of one sidereal day 23 hours 56 minutes and 4 seconds which means that it completes one revolution around earth in exactly the same time.
At this velocity it is synchronous with the earth and becomes geostationary.
From the relationship f centripetal f centrifugal we note that the mass of the satellite m s appears on both sides geostationary orbit is independent of the mass of the satellite.
Such orbit is called geostationary orbit.
A geostationary satellite is a satellite in geostationary orbit with an orbital period the same as the earth s rotation period.
How high above the earth s surface must the geostationary satellite be placed into orbit.
A few objects with small inclinations to.